Type 1 Diabetes: Symptoms, Signs, Causes, Treatment, Cure, Life Expectancy
Type 1 diabetes affects around 10% of the population. Unlike type 2, type 1 appears from childhood, but how is it detected and treated?
What is diabetes?
Discover our latest podcast
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder which is caused by an abnormally high level of glucose in the blood (blood sugar levels) which we call hyperglycemia. The disorder is due to a malfunction in the assimilation system and the way sugars are stored from foods. More precisely, it is linked to a disorder of the hormone that is made by the pancreas cells, insulin.
Definition of type 1 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is the least common form of diabetes as it only affects 5 to 10% of diabetics. Most of the time it appears during childhood or adolescence, which is why it is sometimes referred to as juvenile diabetes.
More under this adMore under this adThis form of diabetes is caused when the pancreas doesn’t produce any or enough insulin to regulate the blood sugar levels. We don’t know why, but the body starts to attack and destroy the beta cells in the pancreas that are in charge of producing insulin. This is why it is known as an autoimmune disorder.
In the absence of this hormone, glucose can’t leave the blood stream and the blood sugar levels stay constantly high even on an empty stomach. The causes of this disorder are still uncertain today but specialists have discovered that genetic factors can be connected as well as some environmental factors.
More under this adMore under this adSymptoms of type 1 diabetes
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes are significantly similar to those of type 2 diabetes; however they are a lot more intense. They include:
- intense thirst
- constantly needing to urinate
- losing a lot of weight quickly despite an increased appetite
- blurred vision
- significant fatigue
- wounds taking longer to heal than normal
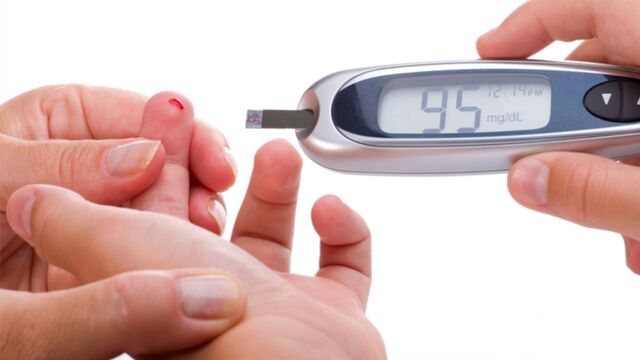
If these symptoms start to appear, it is necessary to consult a doctor who will carry out examinations to confirm whether or not you have diabetes. The tests are done by taking blood samples. If the blood sugar levels are equal to or higher than 1.26g/l on an empty stomach on multiple occasions, diabetes is confirmed.
More under this adMore under this adTreating type 1 diabetes
Diabetes remains to be an incurable disorder. Those who are affected by type 1 diabetes therefore have to inject themselves with insulin daily to compensate for the lack of or impossibility of the pancreas producing it which then lowers the blood sugar levels. Injecting insulin is advised instead of taking it orally so that the hormone is not destroyed by the digestive juices.
If diabetes is to be a part of a normal lifestyle, it is necessary to follow a strict discipline by controlling the blood sugar levels regularly, adopting an appropriate diet regime as well as doing regular physical exercise.
More under this ad