Tuberculosis (TB): Causes, Symptoms, And Treatments
Tuberculosis is a disease caused by Koch's bacillus. Its contagious form, also the most common, is pulmonary tuberculosis. There are also extra-pulmonary forms such as bone tuberculosis or ganglionic tuberculosis. What are their symptoms and their treatments?
What Is Tuberculosis?
Discover our latest podcast
Tuberculosis is a contagious disease caused by a bacterium called Koch's bacillus (BK). Its most common form (85% of cases) is pulmonary tuberculosis (or phthisis) but there are also extra-pulmonary forms such as bone tuberculosis, ganglionic tuberculosis or renal tuberculosis. Once fatal, since the 1950s tuberculosis has had a curative treatment based on antibiotics. However, there are still more than one million fatalities from the disease each year in the world, particularly in Africa and Asia. BCG (Bacille Calmette and Guérin) vaccination is the only way to prevent tuberculosis.
Symptoms Of Tuberculosis
Koch's bacillus may be present in the body for several months or years before it develops. This is called latent tuberculosis. When the disease starts, tuberculosis becomes active and different symptoms appear. In the case of pulmonary tuberculosis the following symptoms may occur:
More under this adMore under this ad- a mild fever
- a persistent cough, with bloody sputum
- pain in the chest to breathe
- shortness of breath
- loss of appetite and weight
- headaches
If clinical signs persist for more than 3 weeks, it is important to consult a doctor.
Bone tuberculosis, also known as Pott's disease, attacks bones, including the spine, hips or knees. It is mainly characterized by a deformation of the spine or the appearance of joint pain. In case of ganglionic tuberculosis, Koch's bacillus is found in lymph nodes. Most of the time, it is cervical ganglia. This results in the presence of abnormal but not painful nodes. They can lead to the formation of an abscess.
Transmission Of Tuberculosis
Pulmonary tuberculosis is the only contagious form of tuberculosis. The spread of bacteria is airborne, in the droplets released into the air during coughing or sneezing and by sputum. People with latent infection are not contagious. Contagion is only possible from the onset of symptoms. In the same way, the transmission period stops after two or three weeks of treatment.
More under this adMore under this adCauses And Risk Factors For Tuberculosis
Some people are more susceptible to TB infection. Those with weakened immune systems due to HIV are among the most common victims. They are about 30 times more likely to develop the disease. Chronic patients (diabetes, cancer) are also at higher risk. Smoking greatly increases the risk of tuberculosis. Indeed, 20% of the listed cases of the disease in the world can be attributed to it. Heavy consumption of alcohol or drugs can also play a role.
The geographical situation has a major influence. More than 95% of TB cases are in developing countries.
Diagnosis Of Tuberculosis
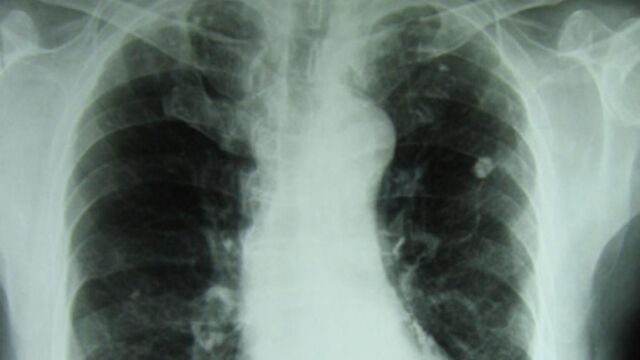
The diagnosis of tuberculosis is based on several examinations. A chest x-ray can be used to assess the condition of the lungs and to look for any lesions. A skin test is also performed. It is an intradermal reaction (IDR) to tuberculin. A drop of tuberculin is injected under the skin in the forearm. After 72 hours, doctors can detect if the patient was in the presence of Koch's bacillus. A laboratory may also analyze a lung sputum specimen. It is cultured several days in a row to detect the presence of the bacillus.
More under this adMore under this adTreatment Of Tuberculosis
The first step in cases of pulmonary tuberculosis is respiratory isolation in a hospital to prevent contagion. It lasts on average between 10 and 20 days, the time that it takes for the fever to pass. Since the infection is bacterial, the treatment of tuberculosis is based on a combination of four antibiotics: isoniazid, rifampicin, ethambutol and pyrazinamide for 2 months and then only isoniazid and rifampicin for the next 4 months. Treatment must be started as soon as possible and followed scrupulously to be effective. Indeed, in case of non-compliance, Koch's bacillus is likely to become resistant to antibiotics, thus severely compromising the cure. In case of relapse or resistance to treatment, corticosteroids may also be used. To overcome malnutrition, dietary supplements may also be necessary.